Project J3-50099
A novel therapeutic strategy for allergic diseases based on epitope-paratope blocking
Research project ARIS
Code: J3-50099
Period 1.10.2023 - 30.9.2026
Head: Assoc Prof Peter Korošec, BSc (Biol), PhD
ARIS classification : Medicine/Microbiology and Immunology
Organisations: University Clinic of Respiratory and Allergic Diseases Golnik; University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Pharmacy
Description of the project
Food allergies are a growing food safety and public health concern that affect up to 8% of children globally, including in Slovenia. That's 1 in 13 children or about 2 students per classroom. Currently, there is no approved drug for treating food allergy and anaphylaxis, nor is there any therapeutic approach to prevent food sensitization, highlighting the critical need for the development of effective primary prevention strategies for food allergy. Strict avoidance of the food allergen is currently the only way to prevent a reaction. Clinical and experimental analyses indicate a pathognomonic role for antigen-induced cross-linking of mast cell-associated lgE leading to rapid mast cell degranulation and release of preformed mediators and enzymes that drive the clinical manifestations associated with food-triggered anaphylaxis. We recently performed biopanning of phage display libraries with anti-peanut lgE's followed by screening and IgE binding experiments. We selected and identified three unique lgEepitope-like peptides (DHPRFNRDNDVA, DHPRYGP, and DHPRFST) of major peanut allergen Ara h 2. Alignment of these lgE-epitope-like peptides showed overlapping with primary Ara h 2 sequence, indicating that these regions could represent the epitopes of Ara h 2. Immunoblot analyses revealed that the lgE-epitope-like peptides bind to lgE from peanut-allergic individuals. Furthermore, employing Basophil activation assay (BAT), we show that lgE-epitope-like peptides blocked Ara h 2-induced human basophil activation (surface CD63 expression). Given these striking datasets, we hypothesize that synthetic lgE epitope-like peptides can suppress lgE-dependent mast cell activation and suppress lgE-mediated food allergy and anaphylaxis. We plan to test our central hypothesis and accomplish the objectives of this application by pursuing the following specific aims:
Aim #1. To assess whether our synthetic lgE-epitope-like peptides can compete and block the binding of Ara h 2 peanut allergen to IgEs paratopes in quantitative ImmunoCAP inhibition assays.
Aim #2. To assess our synthetic lgE-epitope-like peptides efficacy in suppression of lgE-mast cell activation (by epitope-paratope blocking) and induction of peanut-induced anaphylaxis in humanized mast cellular model systems.
Aim #3. (1) To develop, design, synthesize, and screen a new generation peanut-specific synthetic lgE-epitope-like peptides to optimize for potency, specificity, and drug-like properties (lead optimization) by a bioinformatic approach and using peptide microarray immunoassay; (2) Evaluate the peptide profile of individual peanut-allergic patients and select the most desirable peptide candidates; and (3) demonstrate that these personalized selections of peptides more efficiently suppress lgE-mediated reactions in humanized mast cellular model systems.
Validation: For validation of this early-phase proof-of-principle project and applicable protocol for identifying various epitope (peptide) paratope (IgE) interaction, we will select another completely different allergen source, namely major wasp venom allergen Ves v 5. Thus for wasp venom allergen Ves v 5 we will perform biopanning, screening, IgE binding, selection, and mapping of peptides (on a limited scale). We will then generate wasp venom-specific synthetic lgE epitope-like peptides and try to confirm, that also for other allergen sources, peptides can bind to allergen-specific IgE paratopes and suppress effector cell activation.
Project timeline
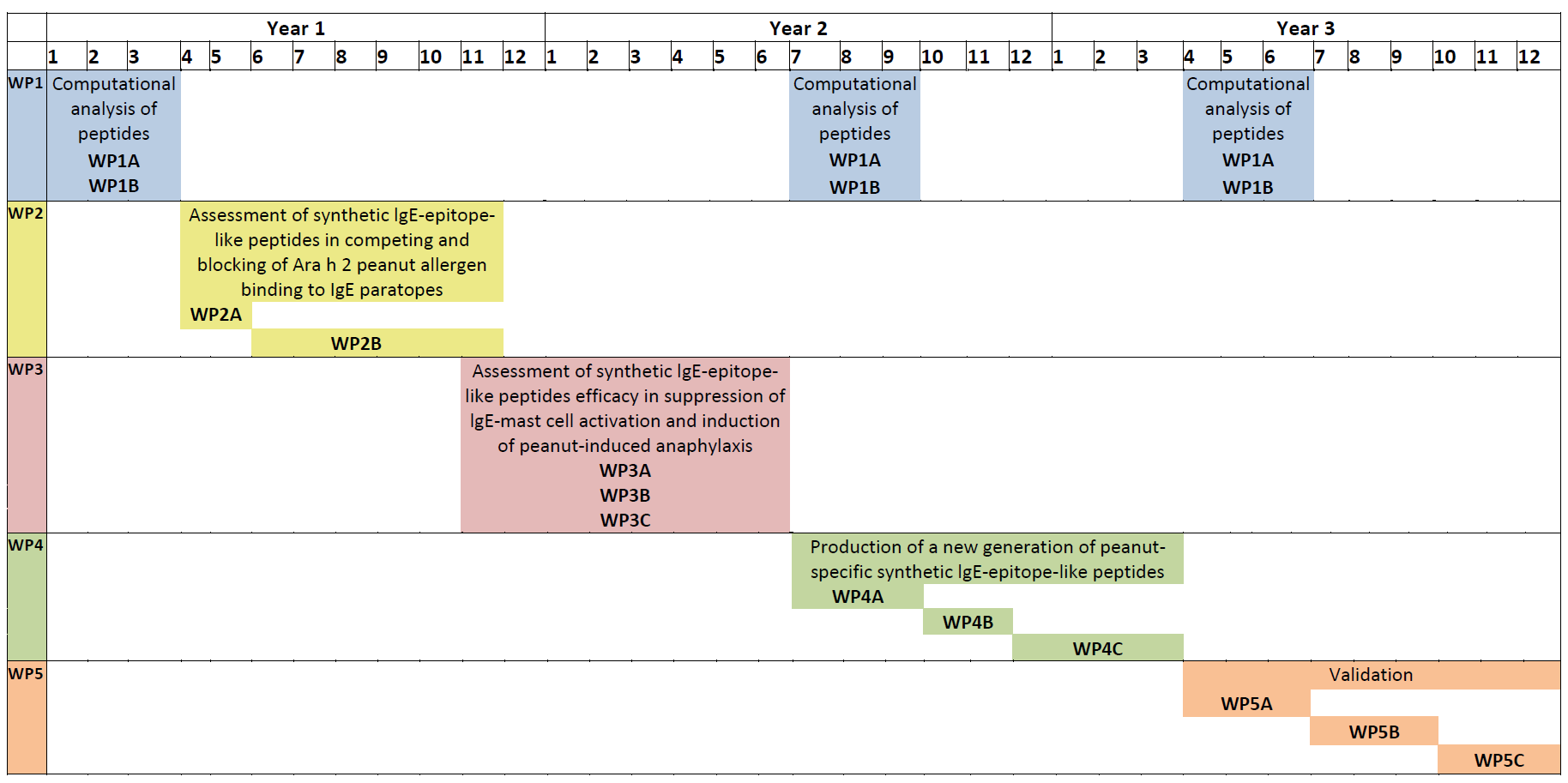
Project work packages and their realization
|
Work package (WP) |
Tasks |
Milestones &Deliverables |
Work distribution |
|
WP1 Computational analysis of peptides
|
WP1A Selection of peptides based on bioinformatic analysis |
Set of IgE epitope-like peptides |
University Clinic Golnik |
|
WP1B Alignment of peptides to primary and 3D structure of the allergen |
Visualization of potential epitope location on the allergen |
||
|
WP2 Assessment of synthetic lgE-epitope-like peptides in competing and blocking of Ara h 2 peanut allergen binding to IgE paratopes |
WP2A Candidate patient sera selection |
Detailed patient data |
University Clinic Golnik & Faculty of Pharmacy (University of Ljubljana) |
|
WP2B ImmunoCAP based inhibition studies |
Quantitative data on the degree of peptide-induced inhibition of Ara h 2 binding to IgEs |
||
|
WP 3 Assessment of synthetic lgE-epitope-like peptides efficacy in suppression of lgE-mast cell activation and induction of peanut-induced anaphylaxis |
WP3A Generation of human mast cells from peripheral blood precursors |
Cultured primary mast cells |
University Clinic Golnik & Faculty of Pharmacy (University of Ljubljana) |
|
WP3B Passive sensitization of cultured primary human mast cells |
Cultured primary mast cells with patient’s IgEs |
||
|
WP3C Mast cells activation assay and testing the blocking activity of synthetic lgE-epitope-like peptides & Measurement of mast cell mediator secretion |
Therapeutic capacity of IgE epitope-like peptides |
||
|
WP 4 Production of a new generation of peanut-specific synthetic lgE-epitope-like peptides |
WP4A Peptide bioinformatic analysis & microarray immunoassay |
Generation of a set of IgE epitope-like peptides |
University Clinic Golnik & Faculty of Pharmacy (University of Ljubljana) |
|
WP4B Allergic individual’s peptide profile evaluation |
Personalized IgE binding profile of each patient |
||
|
WP4C Testing the blocking potential of generated IgE epitope-like peptides in humanized mast cellular model systems |
Confirming or rejecting peptide-induced blocking of mast cell degranulation upon allergen exposure |
||
|
WP 5 Validation |
WP5A Selection of peptides |
Set of IgE epitope-like peptides |
University Clinic Golnik & Faculty of Pharmacy (University of Ljubljana) |
|
WP5B Microarray analysis |
IgE binding profile of each patient |
||
|
WP5C Synthetization and mast cell inhibition test |
Confirming or rejecting peptide-induced blocking of mast cell degranulation upon allergen exposure |


 04 25 69 100
04 25 69 100